


Our team sorts through all blog submissions to place them in the categories they fit the most - meaning it's never been simpler to gain advice and new knowledge for topics most important for you. This is why we have created this straight-forward guide to help you navigate our system.
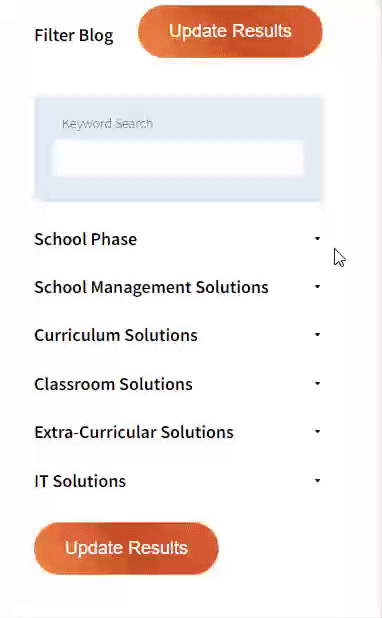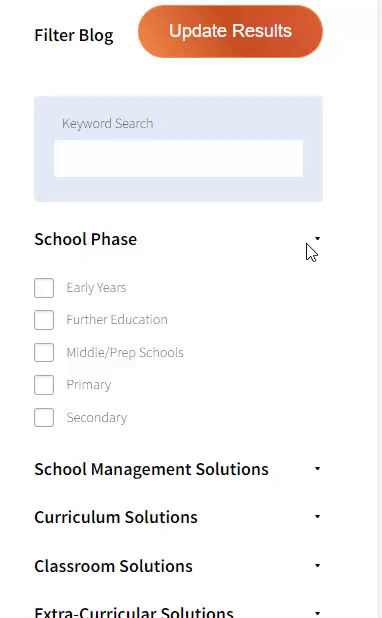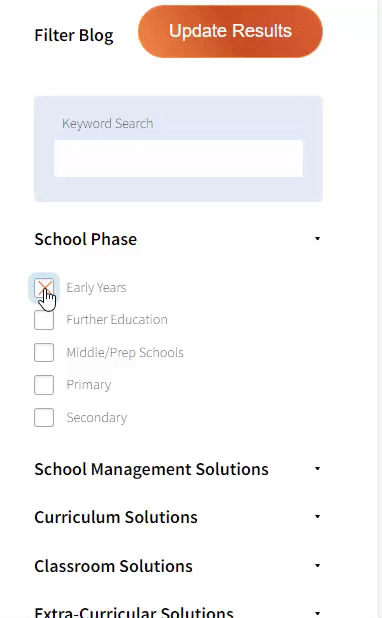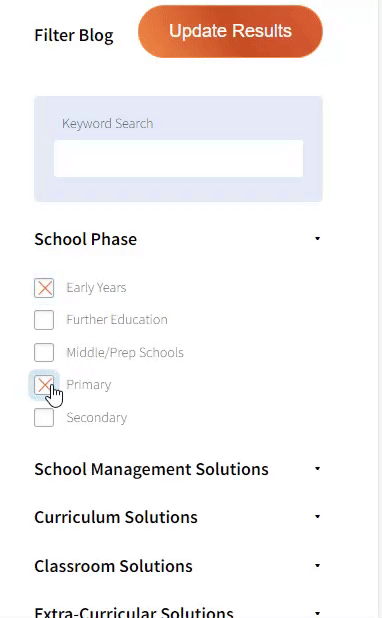
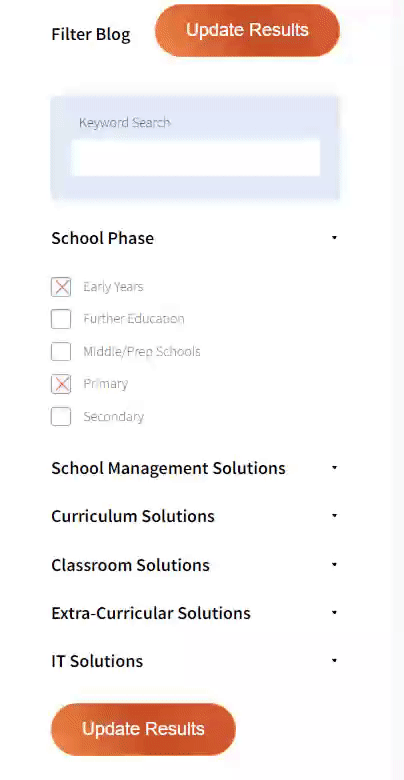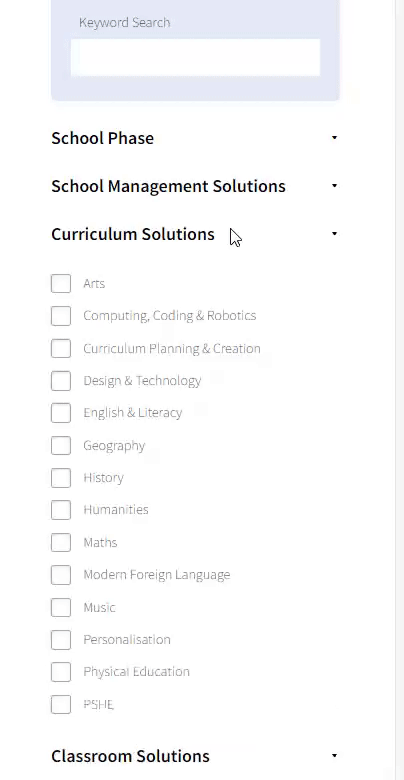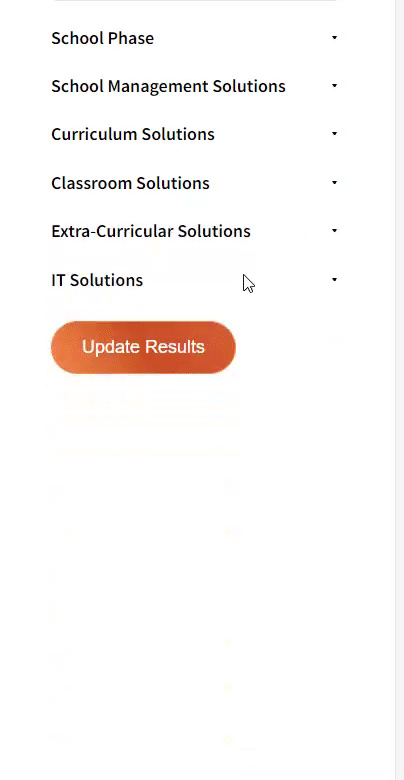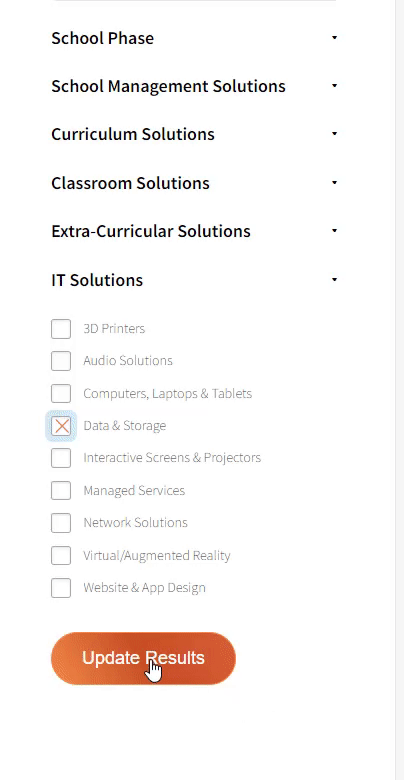
And there you have it! Now your collection of blogs are catered to your chosen topics and are ready for you to explore. Plus, if you frequently return to the same categories you can bookmark your current URL and we will save your choices on return. Happy Reading!
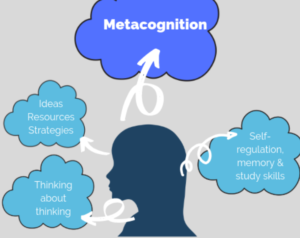
Ever since the Education Endowment Foundation reported that metacognition adds an average of 7 months additional progress and is one of the cheapest strategies based on a strong body of research, many teachers and senior leaders are looking to implement it at their school. But what actually is it? And most importantly, how can we help students develop it?
Metacognition is often defined as ‘thinking about thinking’. However, it is actually much more than that. It covers students’ ability to reflect and critically analyze how they think. Essentially, it is about developing student’s self-awareness, so that they can better monitor, reflect and analyze their own performances. As a result, they become better independent learners.
How Can Schools Develop Student Metacognition?
As metacognition covers a broad range of thinking strategies, there are numerous ways that teachers and schools can help students improve it. We have highlighted four possible ways they can do this.
Before-During-After
Teachers can develop their students’ metacognitive skills by helping them break down the task into three areas; before, during and after. By ensuring that they take time to plan how they are going to do a task, monitor their progress during and evaluate afterwards, their self-awareness, self-reflection and performance next time should all improve. Specifically, this could include:
Model the Correct Thought Processes
If we want to help students identify the correct thinking process, then it may be helpful to model our thought processes. This can be especially helpful for novices at a task, as it provides a step by step guide about how to solve the problem. By breaking it into manageable chunks and actionable steps, the task will seem less daunting and therefore less stressful. Exposing students to their teacher’s thought processes removes any ambiguity and gives them a clear structure from an expert, that they can apply to similar problems.
Use Metacognitive Questioning
Another way in which teachers can enhance their student’s metacognitive skills is by teaching them how to talk to themselves in a helpful and positive way. One seminal study in this area found that by having students ask themselves three simple questions before they started their revision led to them scoring a third of a grade higher. The three questions they had students ask themselves were ‘which resources do I need to help me study?’, ‘why are these resources helpful?’ and ‘how will I use this resource?’ Doing so, improved their self-reflective skills with students reporting they felt more in control of their learning.
Teach Students the Science of Learning
Giving students an awareness of effective strategies that they can use to learn is another way to improve their metacognitive skills. One of the most effective learning strategies is retrieval practice, which requires students to generate an answer to a question. Retrieval practice is effective as it reinforces previous learning which helps create stronger memory traces. This means that actually students shouldn’t do revision in order to do well in a test, but instead do lots of tests to help their revision.
Originally published at: https://www.independentschoolsportal.org
You must be logged in to post a comment.

The author

Read more

Read more

Read more

Read more

Read more

Read more

Read more

Read more


Are you looking for solutions? Let us help fund them! Nexus Education is a community of over 11,000 schools that come together to share best practise, ideas and CPD via online channels and free to attend events. Nexus also offers funding to all school groups in the UK via nexus-education.com


Established in 2011, One Education is a company at the heart of the education world, supporting over 600 schools and academies. Our unique appeal as a provider is in the breadth and synergy of the services we offer, supporting school leaders, teachers and support staff to achieve the best possible outcomes for their pupils and staff.

School Space is a social enterprise that has empowered schools for over 12 years through their profitable and hassle-free lettings services. So far, they’ve generated over £5 million in revenue for education, helping to connect over 200 schools with their local communities.


Unify is an online sales and marketing tool that allows users to create tailored personalised documents in moments.


There’s nothing special about the energy we sell. In fact, it’s exactly the same energy as all our competitors provide. But there is something special about the way we do it. Where others complicate the process, we simplify it. Where others confuse customers with hidden terms, we’re an open book. And where others do all they can to make as much money from their customers as possible, we do all we can to make as little. Everything we do, we do it differently. Our customers are a privilege. One we’ll never take advantage of.


Securus provide market-leading monitoring solutions to safeguard students on ALL devices both online and offline. We also offer a full monitoring service, where we carry out the monitoring on behalf of the school, freeing up valuable staff resources. From the smallest school to large MAT groups, Securus offers safeguarding protection for all!


Bodet Time offers dedicated solutions to education through lockdown alerts, class change systems, PA and synchronised clock systems. Improving time efficiency of the working and school day; ensuring safety through lockdown alerts; increasing communication with customised broadcast alerts.


Robotical makes Marty the Robot - a walking, dancing coding robot that makes programming fun and engaging for learners as young as 5. Our robots come with a full Learning Platform that has complete teaching resources, to make lesson planning a breeze.
Are you aware of the problems with the EEF findings on metacognition. See critique in this article https://gregashman.wordpress.com/2019/09/23/mindset-theory-and-metacognition-are-both-false-idols/